NATO Membership and Expansion

Nato members – The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a political and military alliance of countries from North America and Europe. It was established in the aftermath of World War II to prevent another such conflict. NATO has expanded significantly since its founding, and now has 30 member states.
As NATO members grapple with the implications of the Ukraine conflict, it’s worth noting the insights of George Stephanopoulos , who has covered international affairs extensively. His analysis provides valuable context for understanding the complexities facing NATO members as they navigate this challenging geopolitical landscape.
The process of joining NATO is complex and involves several steps. A country must first submit an application to the alliance, which is then reviewed by the North Atlantic Council, NATO’s governing body. The council must unanimously agree to invite the country to join, and the country must then ratify the North Atlantic Treaty. Once a country has joined NATO, it is committed to defending all other members of the alliance.
Strategic Importance of NATO Expansion, Nato members
NATO expansion has been a controversial issue, particularly in Eastern Europe. Some countries have argued that expanding NATO eastward would provoke Russia and increase the risk of conflict. Others have argued that NATO expansion is necessary to protect Eastern European countries from Russian aggression.
NATO members have come together to address the evolving security landscape, as evidenced by the recent Biden NATO speech. The speech outlined a renewed commitment to collective defense and highlighted the importance of unity among NATO members. The alliance remains a vital forum for cooperation and consultation on security matters, and its members continue to work together to maintain peace and stability.
The debate over NATO expansion is likely to continue for some time. However, there is no doubt that NATO expansion has had a significant impact on the security of Europe.
NATO’s Role in Global Security: Nato Members
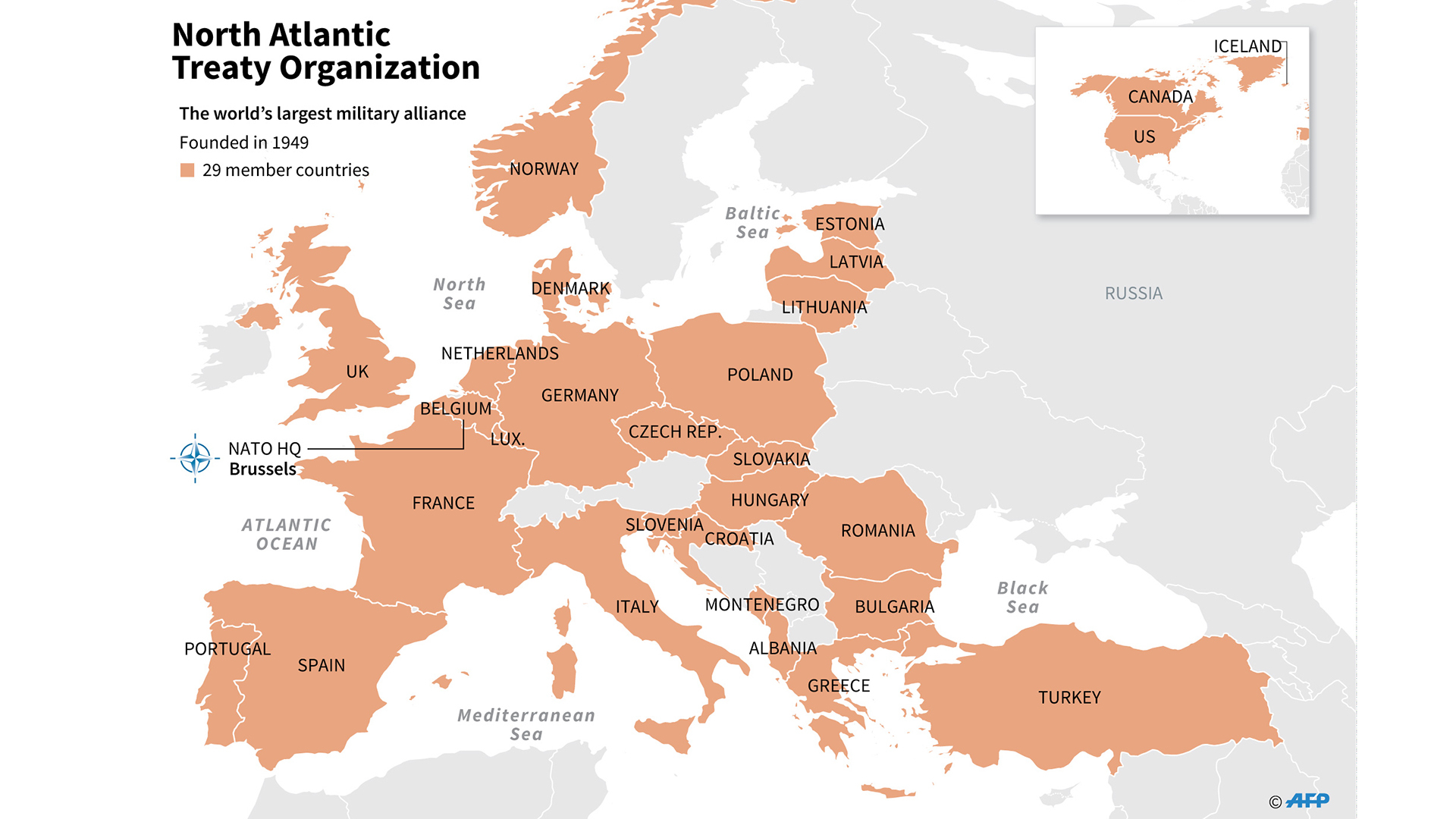
NATO is a political and military alliance of 30 North American and European countries. Its primary objective is to guarantee the freedom and security of its members through political and military means.
NATO has played a significant role in maintaining international peace and security since its founding in 1949. It has been involved in a number of peacekeeping missions and military interventions, including the Kosovo War, the Bosnian War, and the Afghanistan War.
Challenges and Limitations
NATO faces a number of challenges and limitations in addressing global security threats. One challenge is the changing nature of warfare. In recent years, there has been a rise in asymmetric warfare, in which non-state actors use unconventional tactics to attack state actors.
Another challenge is the growing threat of terrorism. NATO has been involved in the fight against terrorism since the 9/11 attacks, but the threat continues to evolve.
NATO also faces limitations in its ability to respond to security threats outside of its member states. The alliance’s mandate is limited to the North Atlantic area, and it can only intervene in other regions with the consent of the United Nations Security Council.
NATO’s Internal Dynamics

NATO is a military alliance of 30 countries from North America and Europe. It was established in the aftermath of World War II to prevent another such conflict. NATO’s internal dynamics are complex, with a variety of factors influencing decision-making and power dynamics.
The United States is the most powerful member of NATO, and it plays a leading role in shaping the alliance’s agenda. Other key members include the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and Italy. These countries have a significant say in NATO’s decision-making, but they must also take into account the interests of the smaller member states.
One of the challenges facing NATO is maintaining unity and consensus among its members. This can be difficult, as the member states have different interests and priorities. For example, the United States is more focused on global security threats, while some European countries are more concerned with regional issues.
Despite these challenges, NATO has been able to maintain unity and consensus for over 70 years. This is due in part to the shared values and interests of the member states, as well as the alliance’s commitment to collective security.
Power Dynamics and Decision-Making
NATO’s decision-making process is based on consensus. This means that all member states must agree on a decision before it can be implemented. This can be a slow and cumbersome process, but it ensures that all members have a say in the alliance’s decisions.
The United States has a significant influence on NATO’s decision-making process. This is due to its military power, economic strength, and diplomatic clout. However, the United States cannot dictate NATO’s decisions. It must take into account the interests of the other member states.
Other key members of NATO, such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and Italy, also have a significant influence on the alliance’s decision-making process. These countries have a long history of cooperation and shared values. They also have a strong commitment to NATO’s collective security.
Challenges of Maintaining Unity and Consensus
One of the challenges facing NATO is maintaining unity and consensus among its members. This can be difficult, as the member states have different interests and priorities. For example, the United States is more focused on global security threats, while some European countries are more concerned with regional issues.
Another challenge facing NATO is the rise of new threats, such as terrorism and cyber warfare. These threats are not easily addressed by NATO’s traditional military capabilities. NATO must adapt to these new threats in order to remain relevant and effective.
Despite these challenges, NATO has been able to maintain unity and consensus for over 70 years. This is due in part to the shared values and interests of the member states, as well as the alliance’s commitment to collective security.