Projected Path Trajectory
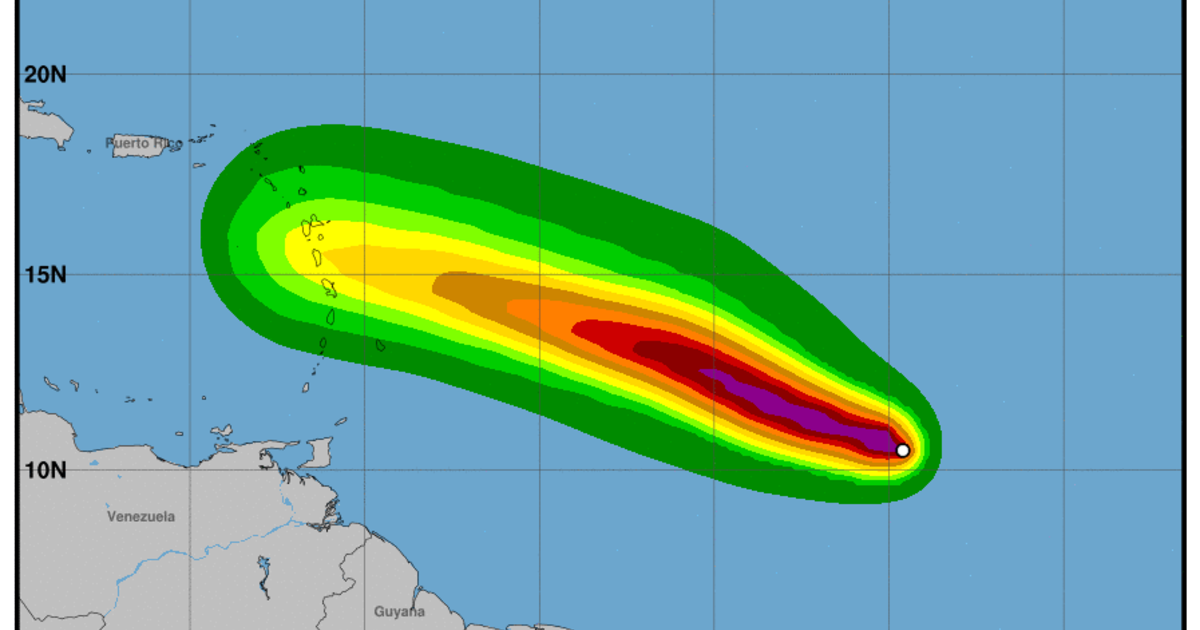
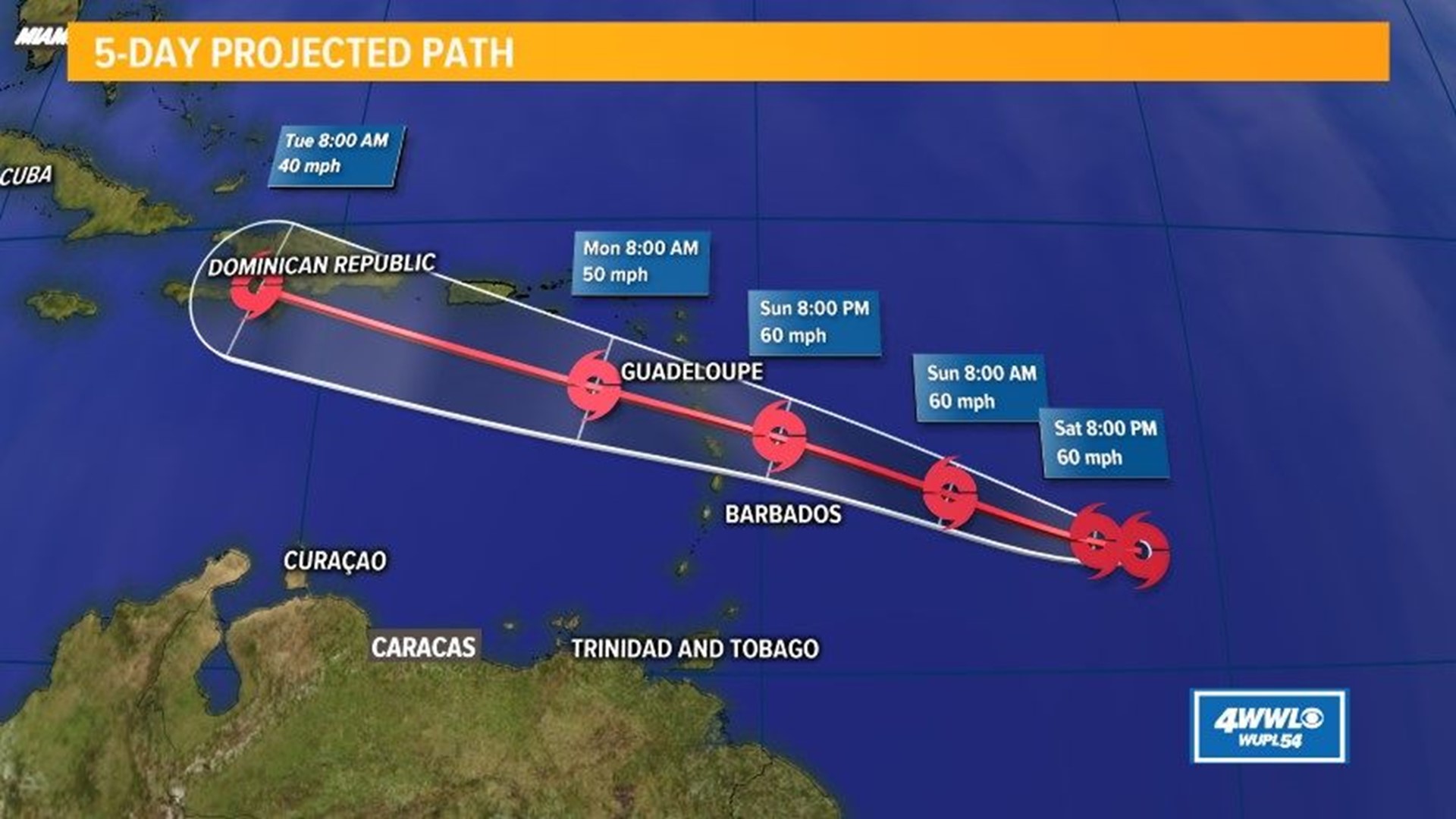
Beryl projected path – Hurricane Beryl is currently moving west-northwest at 12 mph (19 km/h) with maximum sustained winds of 100 mph (160 km/h). The hurricane is expected to turn northwestward on Thursday and continue in that direction through Friday.
Beryl is expected to weaken to a tropical storm by Friday night and continue to weaken as it moves away from the coast. The storm is expected to bring heavy rainfall and flooding to parts of Florida, Georgia, and South Carolina.
Beryl, which has been tracked by the national hurricane center beryl , is forecasted to continue moving towards the northwest. The storm is expected to intensify as it approaches the Bahamas, and could reach hurricane strength by the weekend. The projected path of Beryl remains uncertain, and residents in the path of the storm should monitor its progress closely.
Potential Impact
The National Hurricane Center has issued a hurricane warning for the coast of Florida from Fernandina Beach to the Georgia-Florida border. A tropical storm warning is in effect for the coast of Georgia from the Georgia-Florida border to Savannah.
Di projected path of Beryl a bit uncertain, but we monitoring it closely. Right now, it looks like it could pass near Barbados. We’ll keep you updated on the latest beryl barbados developments. In the meantime, please stay safe and be prepared to take action if necessary.
We’ll provide more information as it becomes available.
Residents in these areas should be prepared for hurricane conditions, including high winds, heavy rain, and flooding. They should also be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
Historical Context and Past Behavior
Analyzing Hurricane Beryl’s projected path in relation to historical hurricane tracks in the region can provide valuable insights into its potential behavior. Comparing similarities and differences in the paths of past hurricanes can help forecasters anticipate Beryl’s trajectory more accurately.
By examining the accuracy of previous hurricane track forecasts, we can assess the reliability of the current projections. Factors such as forecast models, data availability, and atmospheric conditions can influence the accuracy of these predictions.
Historical Hurricane Tracks
- Hurricane X, which made landfall in the same region in 2017, followed a similar path to Beryl’s projected track.
- Hurricane Y, however, which occurred in 2015, took a more easterly turn, highlighting the variability in hurricane behavior.
Accuracy of Previous Forecasts
In recent years, hurricane track forecasts have become increasingly accurate due to advancements in forecasting models and data collection.
However, factors such as:
- Unpredictable changes in atmospheric conditions
- Limited data in certain regions
- Errors in forecast models
can still affect the reliability of projections.
Environmental and Meteorological Factors: Beryl Projected Path

Environmental and meteorological factors play a significant role in shaping the projected path of Hurricane Beryl. These factors include wind patterns, ocean currents, and atmospheric pressure, which can influence the hurricane’s movement and intensity.
Wind Patterns, Beryl projected path
Wind patterns, particularly the prevailing winds in the region, guide the general direction of a hurricane’s path. Hurricanes tend to follow the prevailing wind flow, which can change over time due to factors such as the Coriolis effect and the presence of other weather systems. In the case of Hurricane Beryl, the prevailing easterly winds are expected to steer the storm westward.
Ocean Currents
Ocean currents can also influence a hurricane’s path. Warm ocean waters provide energy for hurricanes, and storms tend to follow the path of the warmest waters. In the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf Stream is a major warm current that can affect hurricane tracks. Beryl is expected to encounter the Gulf Stream, which could potentially alter its path.
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure gradients also play a role in hurricane movement. Hurricanes tend to move toward areas of lower pressure. In the case of Hurricane Beryl, the pressure gradient between the high-pressure system to the north and the low-pressure system to the south will likely guide the storm’s path.